An 18-year-old female was hit by a speeding car while crossing the road.
On examination the patient was conscious and had multiple bruises all over her chest, abdomen, and extremities. Her BP was 90/30 mm Hg, and her pulse was 130/minute. An eFAST exam was performed. Below is the view obtained in the pelvic region. An ultrasound imaging artifact was seen in the image as pointed by the arrows which made the tissue appear brighter.
What is the ultrasound artifact known as?
A. Posterior acoustic shadowing
B. Edge artifact
C. Posterior acoustic enhancement
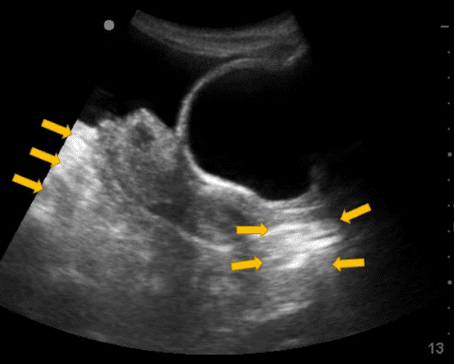
The ultrasound artifact is known as posterior acoustic enhancement.
Explanation
The image shows the region of the tissue posterior to the fluid due to posterior acoustic enhancement. Please see references and images below. If ever in doubt, you can reduce the overall gain to make the image darker to show the artifact more prominently. See figure 1. The posterior acoustic enhancement artifact helps indicate that there is something anteriorly with low ultrasound attenuation. Any structure or organ of pathology with more fluid content allows the ultrasound beam to pass through more easily without significant attenuation as compared to surrounding tissue.
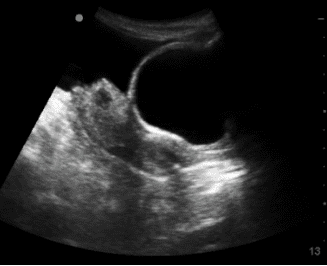
Figure 1. Types of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Saccular/berry aneurysm on the left and fusiform aneurysm on the right. Approximately 94% of aortic aneurysms are fusiform while 90% of cerebral aneurysms are saccular or berry aneurysms.
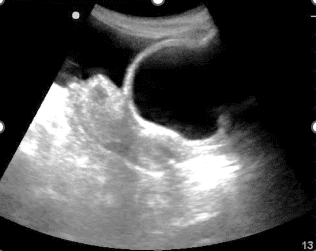
Figure 2. The posterior acoustic enhancement artifact region becomes very echogenic by increasing the overall gain. This should be avoided as some important finding may be missed due to increased noise.
References